TNC Telnet
An AX.25 emulator for TCP connections.
Description
This interface emulates a TNC and makes regular TCP/IP traffic appears like AX.25. So you can connect to a Telnet Ham-Radio BBS or DX Cluster with old MS-DOS Packet Radio software.
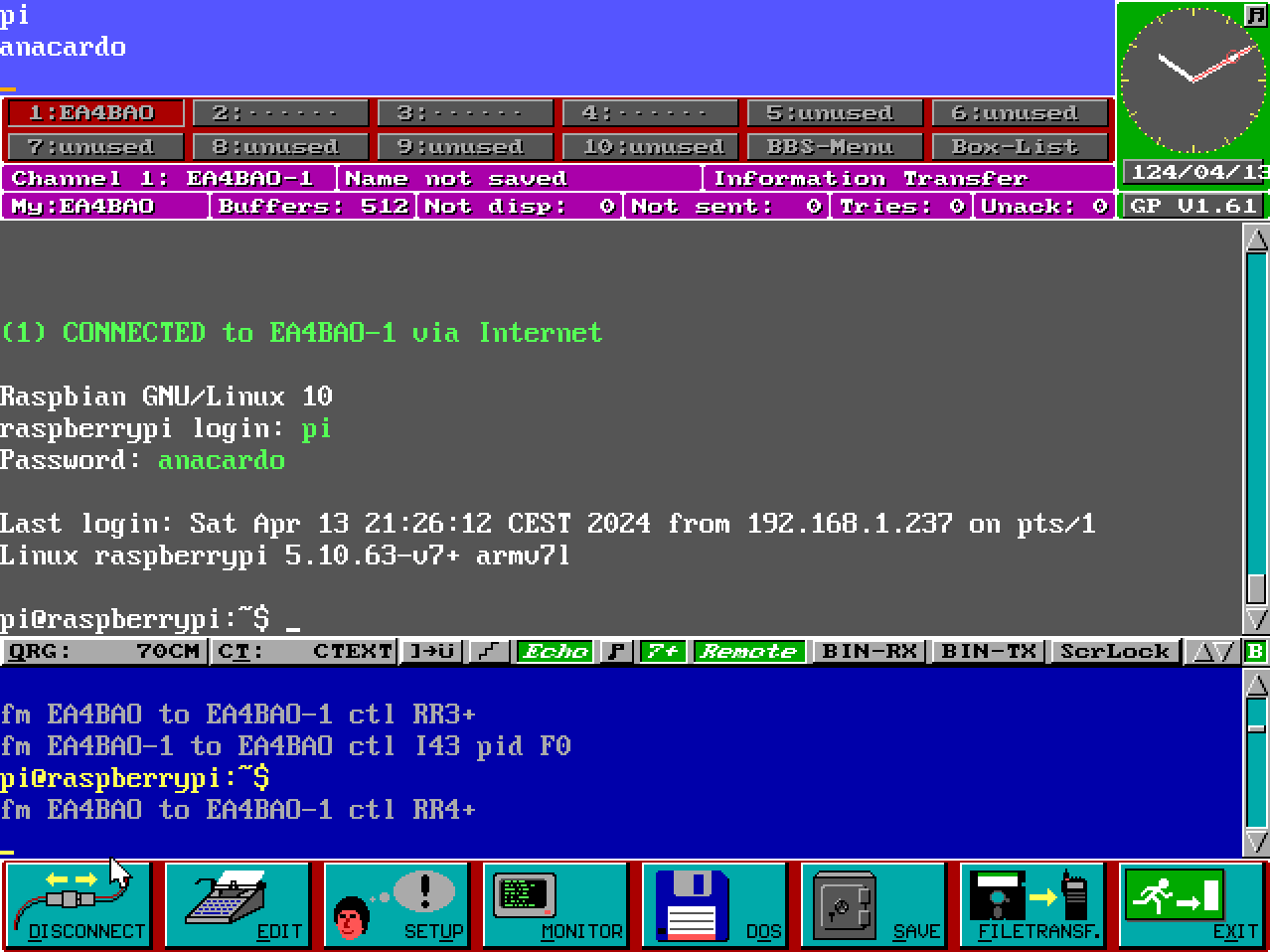
For example Graphic Packet:
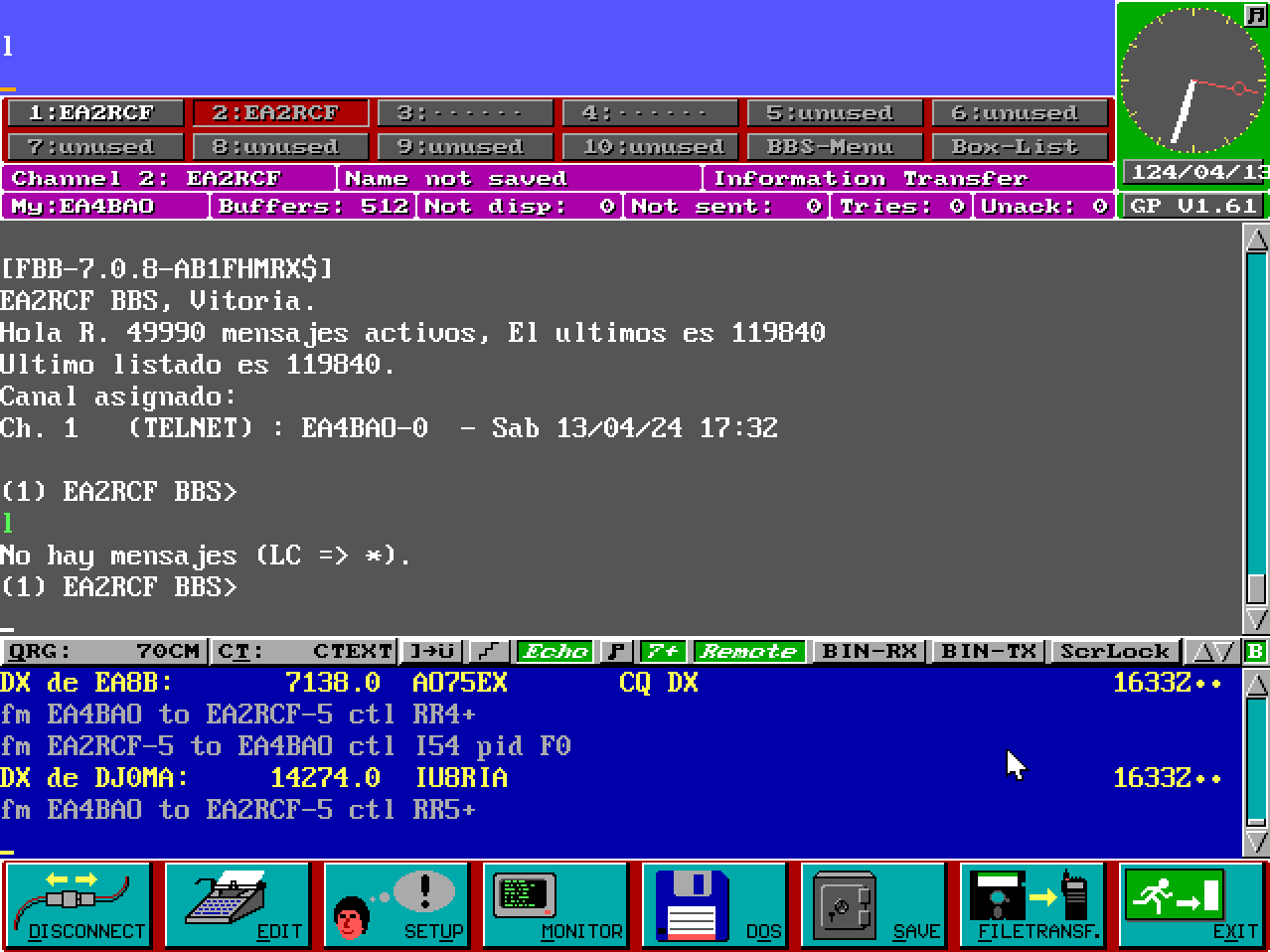
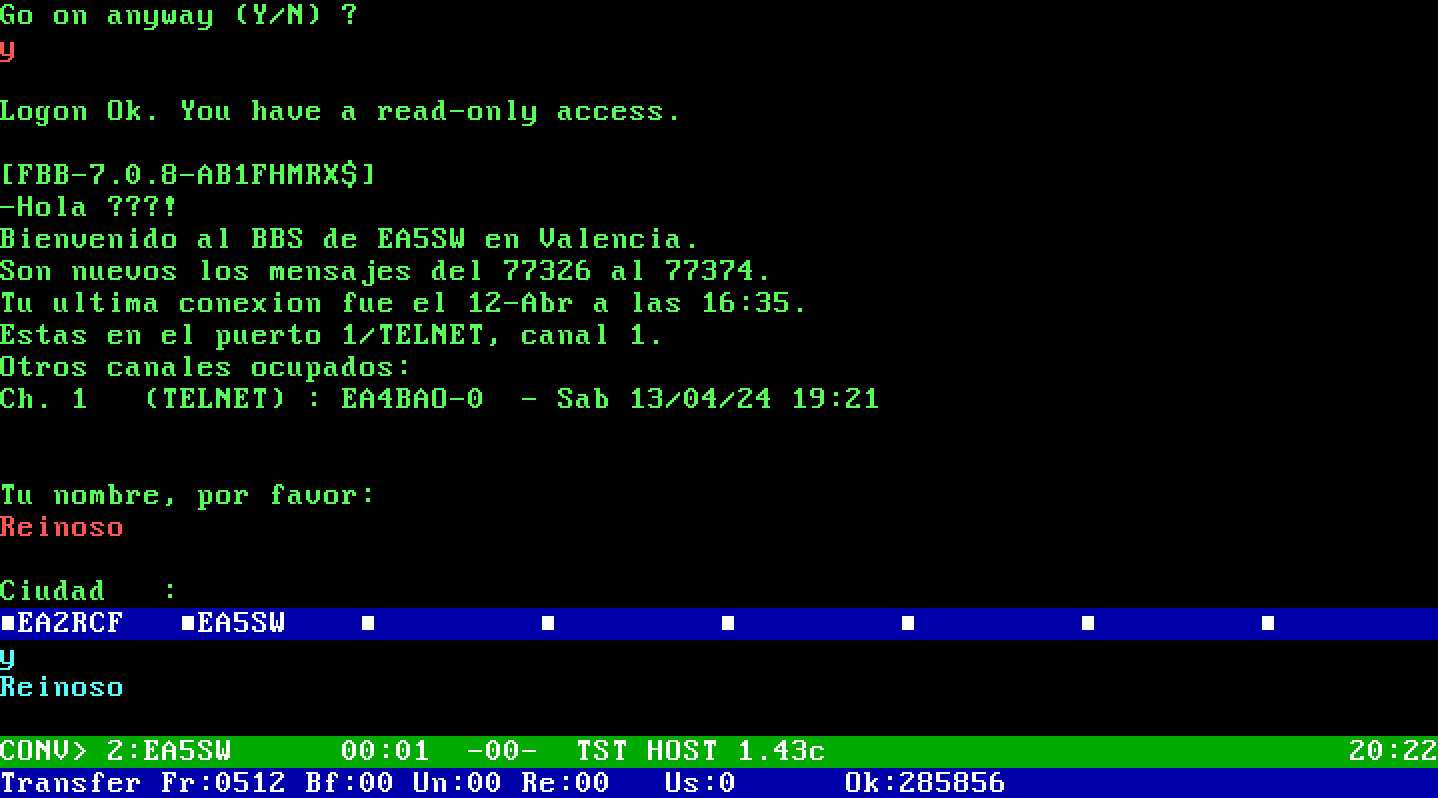
Or TSTHOST:
Monitor traffic is also simulated:
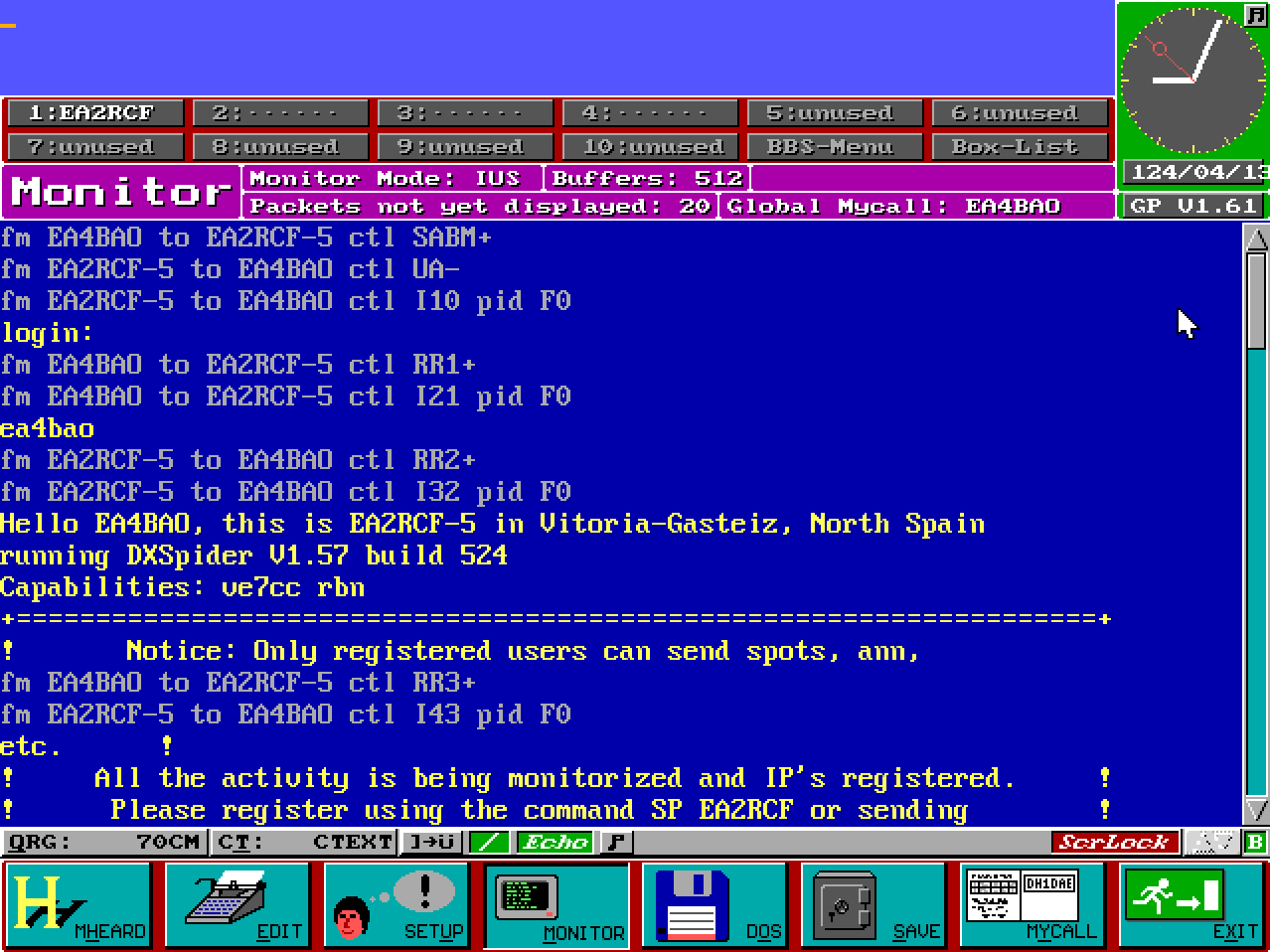
Remember these are actual TCP/IP sockets in disguise.
Usage
Known stations
Edit stations.txt and add data for known stations.
Example:
# Callsign ip or hostname port
EA4BAO localhost 6300
EA2RCF cqnet.dyndns.org 6300
EA2RCF-5 cqnet.dyndns.org 7300
EA5SW ea5sw.ddns.net 6300
Format is space-separated. Empty lines and lines starting with # are ignored.
This file must be in the programs directory. Otherwise, you can set the path with the command line options.
Command line
If you are using Python, launch it that way:
python TNC
Help:
$ python tnc -h
TNCTelnet 1.0
usage: tnc [-h] [--file FILE] [--stations FILE] [--mycall CALLSIGN]
[--jhost1] [--ch N] [-v]
An AX.25 emulator for TCP connections
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--file FILE Device file or named pipe to interact with MS-DOS
box (default: \\.\PIPE\tnc).
--stations FILE JSON file with IP address and TCP port of known
stations (default: stations.txt).
--mycall CALLSIGN My callsign (default: NOCALL).
--jhost1 Start TNC in host mode (default is start in
terminal mode).
--ch N Number of channels (default is 4).
-v Display commands and responses. Multiple times
show more info.
If you are using precompiled binaries, do not open it with double clicking until you are familiar with the software. If something goes wrong, the terminal window will close faster that you have time to read the error.
Setup
Virtual machine
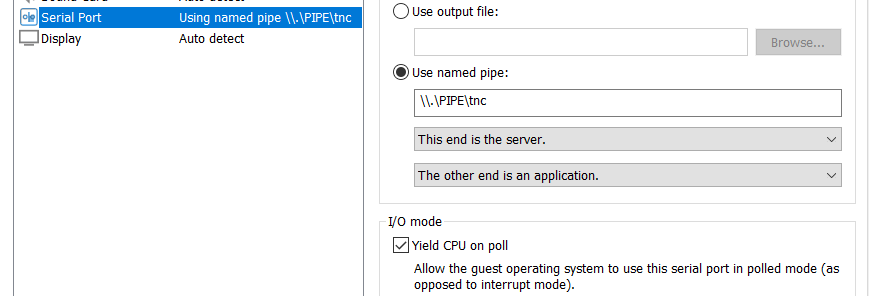
The emulator runs in the host system. Create a virtual machine and configure its serial port as a named pipe (default name is \\.\PIPE\tnc):
Tips for TSTHOST
- Configure CKJ driver using
ckbiocfg. Use COM1, address3F8H, IRQ 4. - Load the driver in memory running
gkjbios. - Launch TSTHOST like this:
TSTHOST /H /C1 /B9600
Tips for Graphic Packet
Edit config.gp and set the serial speed to 1200 bauds for a realistic experience.
Caveats
This software only runs on Windows for now. To run it in Linux you’d need to adapt the channel module. TCP sockets error codes are quite different between Linux and Windows.
Compilation
To create the executable file from the Python sources just run:
pyinstaller.exe --onefile TNC\__main__.py -n TNCTelnet
Misc
Since this is basically a telnet client, you can use it to connect to any Telnet server: